Cellular biology
-
Early Life Events and Maturation of the Dentate Gyrus: Implications for Neurons and Glial Cells
The dentate gyrus (DG), an important part of the hippocampus, plays a significant role in learning, memory, and emotional behavior. Factors potentially influencing normal development of neurons and glial cells in the DG during its maturation can exert long-lasting effects on brain functions. Early life stress may modify maturation of the DG and induce lifelong alterations in its structure and functioning, underlying brain pathologies in adults. In this paper, maturation of neurons and glial cells (microglia and astrocytes) and the effects of early life events on maturation processes in the DG have been comprehensively reviewed. Early postnatal interventions affecting the DG eventually result in an altered number of granule neurons in the DG, ectopic location of neurons and changes in adult neurogenesis. Adverse events in early life provoke proinflammatory changes in hippocampal glia at cellular and molecular levels immediately after stress exposure. Later, the cellular changes may disappear, though alterations in gene expression pattern persist. Additional stressful events later in life contribute to manifestation of glial changes and behavioral deficits. Alterations in the maturation of neuronal and glial cells induced by early life stress are interdependent and influence the development of neural nets, thus predisposing the brain to the development of cognitive and psychiatric disorders.
-
Ca2+-activated KCa3.1 potassium channels contribute to the slow afterhyperpolarization in L5 neocortical pyramidal neurons
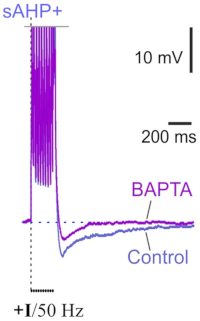
Layer 5 neocortical pyramidal neurons are known to display slow Ca2+-dependent afterhyperpolarization (sAHP) after bursts of spikes, which is similar to the sAHP in CA1 hippocampal cells. However, the mechanisms of sAHP in the neocortex remain poorly understood. Our employee from the Laboratory of Cellular Neurobilogy of Learning identified the Ca2+-gated potassium KCa3.1 channels as contributors to sAHP in ER81-positive neocortical pyramidal neurons. Moreover, their experiments strongly suggest that the relationship between sAHP and KCa3.1 channels in a feedback mechanism underlies the adaptation of the spiking frequency of layer 5 pyramidal neurons. They demonstrated the relationship between KCa3.1 channels and sAHP using several parallel methods: electrophysiology, pharmacology, immunohistochemistry, and photoactivatable probes. Their experiments demonstrated that ER81 immunofluorescence in layer 5 co-localized with KCa3.1 immunofluorescence in the soma. Targeted Ca2+ uncaging confirmed two major features of KCa3.1 channels: preferential somatodendritic localization and Ca2+-driven gating. In addition, both the sAHP and the slow Ca2+-induced hyperpolarizing current were sensitive to TRAM-34, a selective blocker of KCa3.1 channels.
-
A Translational Study on Acute Traumatic Brain Injury: High Incidence of Epileptiform Activity on Human and Rat Electrocorticograms and Histological Correlates in Rats
In humans, early pathological activity on invasive electrocorticograms (ECoGs) and its putative association with pathomorphology in the early period of traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains obscure. Our scientists from the Laboratory of Functional Biochemistry of Nervous System assessed pathological activity on scalp electroencephalograms (EEGs) and ECoGs in patients with acute TBI, early electrophysiological changes after lateral fluid percussion brain injury (FPI), and electrophysiological correlates of hippocampal damage (microgliosis and neuronal loss), a week after TBI in rats. They revealed that epileptiform activity on ECoGs was evident in 86% of patients during the acute period of TBI, ECoGs being more sensitive to epileptiform and periodic discharges. A “brush-like” ECoG pattern superimposed over rhythmic delta activity and periodic discharge was described for the first time in acute TBI. In rats, FPI increased high-amplitude spike incidence in the neocortex and, most expressed, in the ipsilateral hippocampus, induced hippocampal microgliosis and neuronal loss, ipsilateral dentate gyrus being most vulnerable, a week after TBI. Epileptiform spike incidence correlated with microglial cell density and neuronal loss in the ipsilateral hippocampus. Based on these results, our employees concluded that epileptiform activity is frequent in the acute period of TBI period and is associated with distant hippocampal damage on a microscopic level. This damage is probably involved in late consequences of TBI. The FPI model is suitable for exploring pathogenetic mechanisms of post-traumatic disorders
-
Sodium action potentials in placozoa: Insights into behavioral integration and evolution of nerveless animals
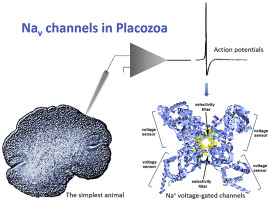
Placozoa are small disc-shaped animals, representing the simplest known, possibly ancestral, organization of free-living animals. With only six morphological distinct cell types, without any recognized neurons or muscle, placozoans exhibit fast effector reactions and complex behaviors. However, little is known about electrogenic mechanisms in these animals. Here, we showed the presence of rapid action potentials in four species of placozoans (Trichoplax adhaerens [H1 haplotype], Trichoplax sp.[H2], Hoilungia hongkongensis [H13], and Hoilungia sp. [H4]). These action potentials are sodium-dependent and can be inducible. The molecular analysis suggests the presence of 5–7 different types of voltage-gated sodium channels, which showed substantial evolutionary radiation compared to many other metazoans. Such unexpected diversity of sodium channels in early-branched metazoan lineages reflect both duplication events and parallel evolution of unique behavioral integration in these nerveless animals